Usage
The nasp program is the pipeline. While you can run the other programs listed in this section directly, they are primarily internal functions of the nasp pipeline.
nasp
The first time you run nasp will typically be without arguments where it will ask you where your files are located and what kinds of analyses you want to run.:
nasp These details will be saved to a [run-name]-config.xml file in the output folder. After the first run, you can use this configuration to repeat or modify the analysis without going through the prompts.:
nasp --config /path/to/[run-name]-config.xml
usage: nasp [-h] [--config CONFIG] [reference_fasta] [output_folder]
| Positional Arguments | (Optional) |
|---|---|
| ReferenceFasta | Path to the reference fasta. |
| OutputFolder | Folder to store the output files. |
| Flags | (Optional) |
|---|---|
| -h, –help | show this help message and exit |
| –config CONFIG | Path to the configuration xml file. |
The following are examples of the nasp commandline prompts:
$ nasp Welcome to NASP version 1.0.0.
NASP will write all the files it creates including any vcf, bam, fasta, tsv, etc to this output folder:
Where would you like output files to be written [nasp_results]? results Where is the reference fasta file you would like to use? ./examples/example_1/reference.fasta
Tip
When entering file paths, try typing the first few characters followed by the Tab key to complete the folder name. Tab completion is only supported if the Python readline module is available.
The nucmer aligner will scan the reference file for duplicate regions creating duplicates.txt and reference.delta in the output reference/ folder.:
Do you want to check the reference for duplicated regions and skip SNPs that fall in those regions [Y]?
If you select none for the job manager, nasp will run the analysis in the background and attempt to balance the job load. If possible, it is better to use a job manager as the analysis can take a long time consuming a lot of computer resources. The defaults queue and commandline arguments should be sufficient.:
What system do you use for job management (PBS/TORQUE, SLURM, SGE/OGE, and 'none' are currently supported) [PBS]? Would you like to specify a queue/partition to use for all jobs (leave blank to use default queue) []? What additional arguments do you need to pass to the job management system []?
External genomes are fasta files not created by NASP such as from a public repository. The NUCmer aligner will be used to align the genomes against the reference genome.:
Do you have fasta files for external genomes you wish to include [Y]? Where are these files located [/home/tgen/NASP]? ./examples/example_1 Would you like to set advanced NUCmer settings [N]?
fastq.gz read files:
Do you have read files you wish to include [Y]? Where are these files located [/home/tgen/NASP]? ./examples/example_1 Would you like to use Trimmomatic to trim your reads first [N]? Y What adapter file are you using for trimming? Would you also like to perform quality trimming [N]? Y What quality trimming parameters do you want to use [SLIDINGWINDOW:5:20]? What is the minimum length read to keep after trimming [80]? Would you like to set advanced ReadTrimmer settings [N]?
This pipeline currently supports three aligners: BWA, Novoalign, and SNAP. You can also provide pre-aligned BAM files, and you can choose as many options as you want. Would you like to run BWA samp/se [N]?* Would you like to run BWA mem [Y]? Would you like to set advanced BWA-mem settings [N]? Would you like to run Bowtie2 [Y]? Would you like to set advanced Bowtie2 settings [N]? Would you like to run Novoalign [Y]? Would you like to set advanced Novoalign settings [N]? Would you like to run SNAP [N]?* Do you have pre-aligned SAM/BAM files you wish to include [N]?
This pipeline currently supports four SNP callers: GATK, SolSNP, VarScan, and SAMtools, and you can provide VCF files. You can choose as many options as you want. Would you like to run GATK [Y]? Unable to find 'GenomeAnalysisTK.jar', please enter the full path to 'GenomeAnalysisTK.jar': /packages/GenomeAnalysisTK/2.7-2/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar Would you like to set advanced GATK settings [N]? Would you like to run SolSNP [N]? Would you like to run VarScan [Y]? Would you like to set advanced VarScan settings [N]? Would you like to run SAMtools [Y]? Would you like to set advanced SAMtools settings [N]? Unable to find 'CreateSequenceDictionary.jar', please enter the full path to 'CreateSequenceDictionary.jar': /packages/tnorth/bin/CreateSequenceDictionary.jar
Do you have pre-called VCFfiles you wish to include [N]?
This pipeline can do filtering based on coverage. If you do not want filtering based on coverage, enter 0. What is your minimum coverage threshold [10]? This pipeline can do filtering based on the proportion of reads that match the call made by the SNP caller. If you do not want filtering based on proportion, enter 0. What is the minimum acceptable proportion [0.9]?
See matrix for commandline arguments you can pass to the MatrixGenerator. This is not typically required.:
Would you like to set advanced MatrixGenerator settings [N]?
In addition to the statistics, bestsnp, missing data, and master matrices, nasp matrix, will create master_masked matrices in the output matrices/ folder. See matrix for output details.
Do you want to create a master_masked matrix that includes all positions with low-quality positions that failed the coverage or proportion filter masked with an 'N' [N]?
format_fasta
Reformats a fasta to be split 80 characters per line, with system line-endings.:
usage: format_fasta [-h] --inputfasta INPUTFASTA --outputfasta OUTPUTFASTA
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit --inputfasta file Path to input fasta. --outputfasta file Path to output fasta.
find_duplicates
Scans the reference genome for duplicate regions using the NUCmer aligner.:
usage: find_duplicates [-h] [--nucmerpath NUCMERPATH] --reference REFERENCE
| -h, --help | show this help message and exit |
| --nucmerpath NUCMERPATH | |
| Path to the ‘nucmer’ executable. | |
| --reference REFERENCE | |
| Path to the reference fasta file. | |
frankenfasta
usage: nasp frankenfasta [filtered mummer delta]
Frankenfasta creates a fasta 1-to-1 position aligned with a reference fasta by combining a sample fasta with a nucmer alignment delta file.
How it works:
To start with, a list of reference fasta contigs and their lengths are read from the delta file. This is used to create a fasta where all positions are masked with ‘X’.:
>Contig Description XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
The delta alignments are used to copy positions from the sample fasta into their corresponding positions in the reference fasta.:
>Contig Description XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAAAAAXAAXXAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAAAAGTTACTTTCATTAATAGAGCAAAATTTATTAATTATACTTTTTACACAAAAAACAAAGAGAGGATCGACCTTTTC TATTCATTCTTTAAACTACAGATTCTTTATAAAAAAATTTAACGACGTTGAGAGTAGACATGAGCGAAAGCACGGGTAGT AGCACGCTTCAACTTGGATTGAGCGGCCTTGAGGTCATCAGCTTGAGCATCGTCAGCGGTGAGTTCCATCAATTCCATGG CTTCAGCGAGAGCAGTTTCAATGGCTTCACGGTCACCACGACGGAGCTTCATGTTGACGTTAGGGTCAGAGATGTTGTTC TCAACTTGGTAGACGTAAGATTCAAGATCTTGCTTGGCTTGTACAACGGCTTCACGTTGCTTGTCAGATTCAGCATTCTT TTCAGCATCTTGAACCATACGTTCGATATCAGCAGCAGAGAGACGAGTAGAGTTGGAGATGGTGACATCAGCCTTGCGAC CAGTGGTCTTGTCTTGAGCAGTGACCTTCAAGATACCATTGGCATCCAAGTCAAAGGTACAGAGAAGTTCAGGGGTACCA CGGGGAGCAGGGATAAGACCAGAGAGAGAGAACTCACCGAGAAGGTTGTTTTCCTTGGTCATCAAACGTTCACCTTCGTA GACAGGGAAAGTGACAGTGGTTXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
‘X’ indicates the absence of calls. Either no sequence aligned to the position, or it was a deletion.
‘N’ indicates uncertain calls. Two alignments with different calls may have mapped to the same position.
Pre-release versions of NASP used a ‘.’ to differentiate deletions from missing data.
matrix
usage: nasp matrix --dto-file matrix_dto.xml
Matrix aggregates the VCF and Frankenfasta files from the NASP pipeline into .tsv matrix and stats file summaries which may be parsed for further analysis.
Given the –dto-file flag, all other flags are optional overrides. A reference fasta and vcf/frankenfasta files are always required, either from the dto or listed on the command line.
| --dto-file | Path to the matrix_dto.xml file |
| --num-threads | Max number of CPUs that can be executing simultaneously (default: all) |
| --reference-fasta | |
| Path to the reference.fasta against which samples are compared | |
| --reference-dups | |
| Path to the duplicates.txt file marking duplicated positions | |
| --stats-folder | Path to the output folder for statistics (default: ./) |
| --matrix-folder | |
| Path to the output folder for matrices (default: ./) | |
| --minimum-coverage | |
| Filter positions below this coverage/depth threshold (default: 0) | |
–minimum-proportion Filter positions below this proportion threshold (default: 0.0) –withallrefpos Include the withallrefpos.tsv matrix
Matrices
matrix will write the following matrices to the output matrices/ folder in tsv, snpfasta, and vcf formats:
| Matrix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Master Matrix | All positions |
| Master Masked | Positions that failed the coverage or proportion filter are masked with an ‘N |
| Best SNP | SNPs that passed the General Stats quality_breadth filter |
| Missing Data | Positions that passed the General Stats quality_breadth filter |
- The conventions used for what data is stored are as follows:
- Genomes:
- A, C, G, T, U: The respective call.
- N: Called “N” according to upstream analysis tools.
- X: Not called by upstream analysis tools.
- . or empty string: A deletion relative to reference.
- String of length >1: An insertion relative to reference.
- Any other single letter: A degeneracy.
- Duplicate region data:
- 0: Position not in a region that is duplicated within the reference.
- 1: Position is in a region that is duplicated.
- -: Duplicate checking at this position was skipped by the user.
- Filters:
- Y: This position passed its filter.
- N: This position failed its filter.
- ?: The filter could not be checked, and so the position is assumed to have failed.
- -: The filter was not applicable, or skipped, or could not be checked for a known reason, and so is assumed to have passed.
Statistics
matrix collects sample analysis statistics and stores them as TSV files in the output statistics/ folder. The tables below list and describe their columns.
General Stats include statistics gathered for all samples relative to the reference genome.
| general_stats.tsv | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Contig | The contig name defined by its source file. |
| reference_length | Total number of positions found in the the reference genome. |
| reference_clean | Number of positions called A/C/G/T in the reference genome. |
| reference_clean (%) | Percentage of above. |
| reference_duplicated | Number of reference contig positions in a duplicated region. |
| reference_duplicated (%) | Percent of the reference contig |
| all_called | Number of positions where the base was called A/C/G/T in all samples. |
| all_called (%) | Percentage of above. |
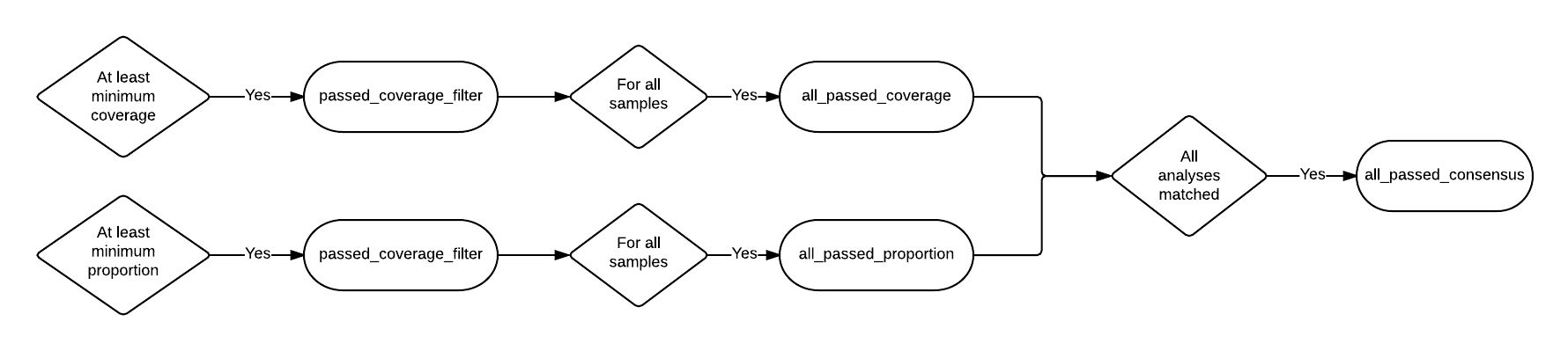
| all_passed_coverage | Number of positions that passed the coverage filter in all samples. [1] |
| all_passed_coverage (%) | Percentage of above. |
| all_passed_proportion | Maximum number of positions that passed the proportion filter in all samples. [1] |
| all_passed_proportion (%) | Percentage of above. |
| all_passed_consensus | Number of positions where all analyses agreed for all samples. |
| all_passed_consensus (%) | Percent of positions where all samples matched the reference contig. |
| quality_breadth | Number of positions called A/C/G/T and passed all filters for all samples. |
| quality_breadth (%) | Percentage of above. |
| any_snps | Number of positions that had a SNP called A/C/G/T in any sample. |
| any_snps (%) | Percentage of above. |
| best_snps | Number of positions that had a confident SNP called A/C/G/T in any sample. |
| best_snps (%) | Percentage of above. |
Sample Stats include statistics for each sample/analysis combination.
| sample_stats.tsv | Column Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Sample | Sample name based on the filename. |
| Sample::Analysis | Sample/Aligner/SNP Caller combination. |
| was_called | Number of positions called A/C/G/T. |
| was_called (%) | Percentage of above. |
| passed_coverage_filter | Number of positions that passed the coverage filter. [1] |
| passed_coverage_filter (%) | Percentage of above. |
| passed_proportion_filter | Number of positions that passed the proportion filter. [1] |
| passed_proportion_filter (%) | Percentage of above. |
| quality_breadth | Number of positions called A/C/G/T and passed all filters. [1] |
| quality_breadth (%) | Percentage of above. |
| called_reference | Number of positions that matched the reference. |
| called_reference (%) | Percentage of above. |
| called_snp | Number of positions that differed from the reference. |
| called_snp (%) | Percentage of above. |
| called_dgen | Number of positions not called A/C/G/T. [2] |
| called_dgen (%) | Percentage of above. |
| [1] | (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) If the filter could not be checked for a known reason, such as with a FASTA file, it is assumed to have passed. |
| [2] | Includes degeneracies, unknown, and uncalled |
The pseudo-flowcharts below reflect relationships between the statistics where each terminal node is a statistics column. Click the image to view it in detail.

Example Statistics
| Contig | reference_length | reference_clean | reference_clean (%) | reference_duplicated | reference_duplicated (%) | all_called | all_called (%) | all_passed_coverage | all_passed_coverage (%) | all_passed_proportion | all_passed_proportion (%) | all_passed_consensus | all_passed_consensus (%) | quality_breadth | quality_breadth (%) | any_snps | any_snps (%) | best_snps | best_snps (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Genome | 3977 | 3977 | 100.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 5 | 0.13% | 5 | 0.13% |
| 500WT1_test | 3977 | 3977 | 100.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 5 | 0.13% | 5 | 0.13% |
The [any] and [all] rows track statistics collected for any and all analysis combinations on each sample. The first two [any] and [all] rows are special because they track statistics collected for any and all analysis combinations for all samples.
| Sample | Sample::Analysis | was_called | was_called (%) | passed_coverage_filter | passed_coverage_filter (%) | passed_proportion_filter | passed_proportion_filter (%) | quality_breadth | quality_breadth (%) | called_reference | called_reference (%) | called_snp | called_snp (%) | called_degen | called_degen (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [any] | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3968 | 99.77% | 5 | 0.13% | 0 | 0.00% | |
| [all] | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3968 | 99.77% | 5 | 0.13% | 0 | 0.00% | |
| example_1_L001 | [any] | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3968 | 99.77% | 5 | 0.13% | 0 | 0.00% |
| example_1_L001 | [all] | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3968 | 99.77% | 5 | 0.13% | 0 | 0.00% |
| example_1_L001 | example_1_L001::Bowtie2,GATK | 3974 | 99.92% | 3974 | 99.92% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3973 | 99.90% | 3968 | 99.77% | 5 | 0.13% | 0 | 0.00% |
Running NASP with the example data and default options on a PBS cluster results in the following output.:
nasp_results ├── bowtie2 │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2.bam │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2.bam.bai │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2.mpileup │ ├── nasp_bowtie2_example_1_L001.e293242 │ └── nasp_bowtie2_example_1_L001.o293242 ├── bwamem │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem.bam │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem.bam.bai │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem.mpileup │ ├── nasp_bwamem_example_1_L001.e293241 │ └── nasp_bwamem_example_1_L001.o293241 ├ ── external │ ├── example_1.delta │ ├── example_1.fasta │ ├── example_1.filtered.delta │ ├── example_1.frankenfasta │ ├── nasp_AssemblyImporter_example_1.e293240 │ └── nasp_AssemblyImporter_example_1.o293240 ├── gatk │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2-gatk.vcf │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2-gatk.vcf.idx │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem-gatk.vcf │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem-gatk.vcf.idx │ ├── example_1_L001-novo-gatk.vcf │ ├── example_1_L001-novo-gatk.vcf.idx │ ├── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-bowtie2.e293247 │ ├── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-bowtie2.o293247 │ ├── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-bwamem.e293244 │ ├── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-bwamem.o293244 │ ├── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-novo.e293250 │ └── nasp_gatk_example_1_L001-novo.o293250 ├── matrices │ ├── bestsnp_matrix.snpfasta │ ├── bestsnp_matrix.tsv │ ├── bestsnp_matrix.vcf │ ├── master_matrix.tsv │ ├── missingdata_matrix.snpfasta │ ├── missingdata_matrix.tsv │ └── missingdata_matrix.vcf ├── matrix_dto.xml ├── nasp_matrix.e293253 ├── nasp_matrix.o293253 ├── novo │ ├── example_1_L001-novo.bam │ ├── example_1_L001-novo.bam.bai │ ├── example_1_L001-novo.mpileup │ ├── nasp_novo_example_1_L001.e293243 │ └── nasp_novo_example_1_L001.o293243 ├── reference │ ├── duplicates.txt │ ├── nasp_DupFinder.e293239 │ ├── nasp_DupFinder.o293239 │ ├── nasp_index.e293238 │ ├── nasp_index.o293238 │ ├── reference.1.bt2 │ ├── reference.2.bt2 │ ├── reference.3.bt2 │ ├── reference.4.bt2 │ ├── reference.delta │ ├── reference.dict │ ├── reference.fasta │ ├── reference.fasta.amb │ ├── reference.fasta.ann │ ├── reference.fasta.bwt │ ├── reference.fasta.fai │ ├── reference.fasta.idx │ ├── reference.fasta.pac │ ├── reference.fasta.sa │ ├── reference.rev.1.bt2 │ └── reference.rev.2.bt2 ├── nasp_results-config.xml ├── runlog.txt ├── samtools │ ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2-samtools.vcf │ ├── example_1_L001-bwamem-samtools.vcf │ ├── example_1_L001-novo-samtools.vcf │ ├── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-bowtie2.e293249 │ ├── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-bowtie2.o293249 │ ├── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-bwamem.e293246 │ ├── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-bwamem.o293246 │ ├── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-novo.e293252 │ └── nasp_samtools_example_1_L001-novo.o293252 ├── statistics │ ├── general_stats.tsv │ └── sample_stats.tsv └── varscan ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2-varscan.vcf ├── example_1_L001-bowtie2.txt ├── example_1_L001-bwamem-varscan.vcf ├── example_1_L001-bwamem.txt ├── example_1_L001-novo-varscan.vcf ├── example_1_L001-novo.txt ├── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-bowtie2.e293248 ├── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-bowtie2.o293248 ├── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-bwamem.e293245 ├── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-bwamem.o293245 ├── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-novo.e293251 └── nasp_varscan_example_1_L001-novo.o293251
Most of the files are either from the external analysis programs or STDIN and STDOUT files created by the PBS cluster for each job. The files in this example created directly by NASP include:
- The matrices and statistics folders from the matrix script
- runlog.txt which includes the terminal commands used to run the external analysis programs
- nasp_results-config.xml
- matrix_dto.xml
- reference/duplicates.txt
- external/example_1.frankenfasta
The other files are organized into folders based on the analysis tool used to create them.